Enterprise Network Best Practices For Performance, Security And Scalability
The Business Case for Enterprise-Grade Networks
Why Enterprises Need a Robust Network
The need for high-performance networking is growing faster than ever. Video conferencing, cloud computing, and VR have already shown how much strain modern applications place on networks. Now, with large language models (LLMs) and AI entering the picture, the demands will climb even higher.
Training LLMs requires sustained high bandwidth, ultra-low latency, and virtually zero packet loss to move massive amounts of data across GPUs. Any congestion or delay can slow or even stall training. And once deployed, these models still depend on low latency to deliver fast, responsive insights, critical for real-time and interactive applications where every millisecond counts.
Beyond AI, high-performance networks remain essential across industries:
Finance, healthcare, and manufacturing rely on real-time data for critical decisions.
Edge computing demands localized, low-latency processing to optimize performance.
Cloud adoption continues to grow, requiring scalable, resilient connectivity.
As networks grow more complex, centralized management and automation are essential if you require agility, error reduction, and consistent performance. At the same time, rising cyber threats demand integrated, automated security to safeguard sensitive data and critical infrastructure.
In a nutshell, a future-ready network is more than just shiny infrastructure, it’s a competitive advantage. Organizations that invest in network infrastructure will scale faster, innovate more easily, and stay ahead in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
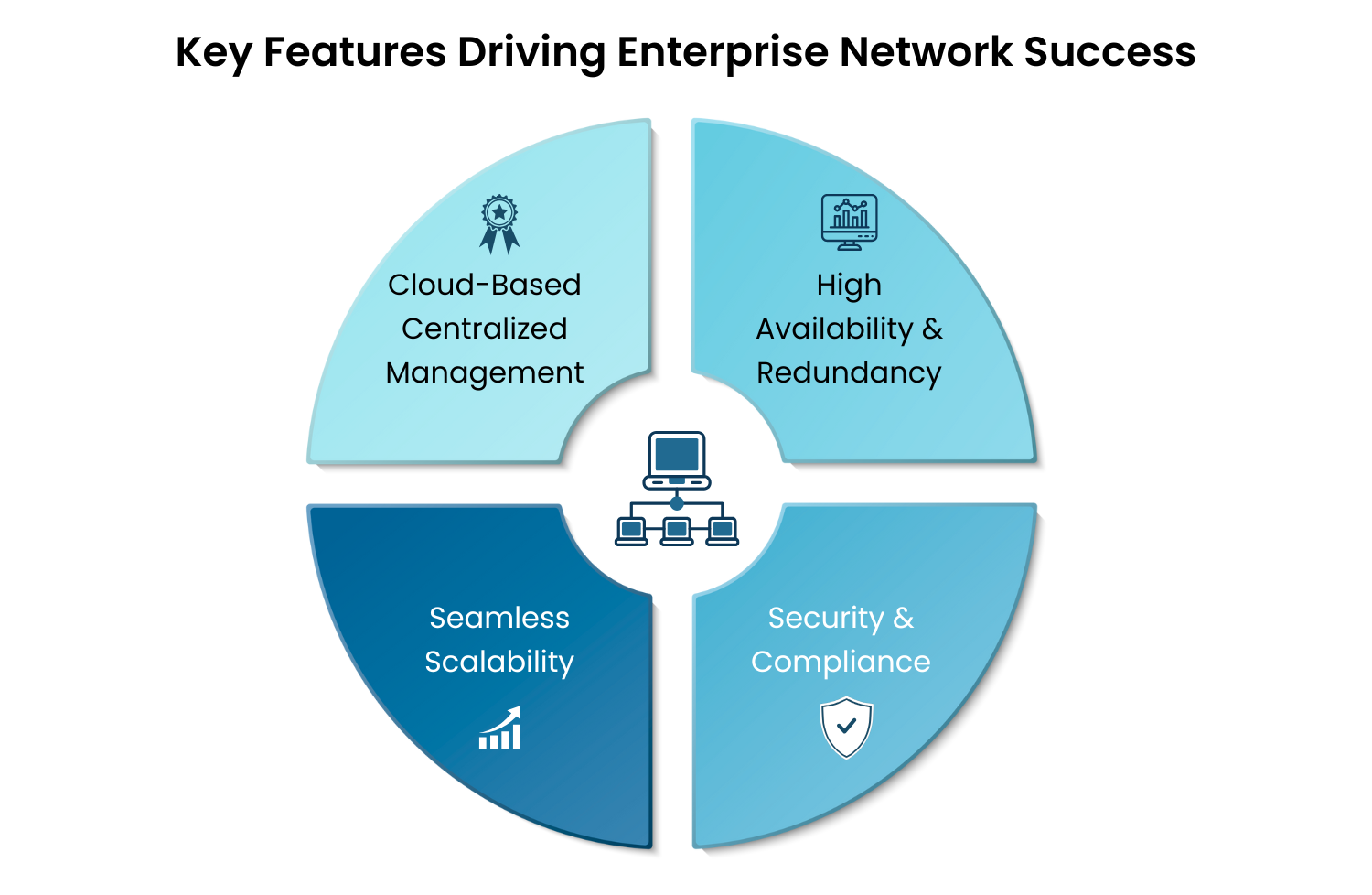
Key Features That Drive Enterprise Network Success
A high-performance enterprise network is a strategic asset that drives agility, security, and competitive advantage. Here are the essentials every modern enterprise needs:
1. Cloud-Based Centralized Management
Cloud-managed networking combines on-premises devices with cloud-based control, giving IT teams the ability to configure, monitor, and troubleshoot from anywhere. Features like zero-touch provisioning and centralized dashboards make multi-site deployments seamless, reduce operational costs, and streamline management at scale.
2. Security & Compliance
As cyber threats and regulatory demands grow, networks must be secure by design. Enterprise-grade solutions integrate next-generation firewalls, intrusion prevention, Zero Trust access, MFA, and AI-driven threat detection to protect sensitive data in real time. Built-in compliance support (HIPAA, PCI-DSS, SOC 2, GDPR, etc.) reduces audit burden while strengthening network resilience against attacks.
3. High Availability & Redundancy
Downtime is no longer an option. Features like automatic failover, redundant uplinks, and self-healing wireless mesh ensure uninterrupted connectivity, even during hardware failures. With cloud backups, new devices can be swapped in and auto-configured instantly, keeping users productive and operations seamless.
4. Seamless Scalability
Growth requires networks that expand without friction. Cloud-first management makes it easy to add new offices, devices, or Wi-Fi coverage from a single dashboard. Dynamic optimization keeps performance strong in high-density environments, while automation ensures networks adapt quickly to business needs.
In summary, a future-ready enterprise network is secure, resilient, scalable, and easy to manage. By investing in these capabilities, businesses position themselves to grow faster, reduce risk, and deliver the seamless digital experiences their employees and customers expect.
Key Factors for Optimizing Enterprise-Grade Networks
1. Network Design & Topology Best Practices
A well-structured network is the foundation for scalability, performance, and security. While cloud-based management simplifies administration, strong design and topology remain critical. By adopting a hierarchical architecture, applying segmentation strategies, and following traffic optimization best practices, enterprises can eliminate bottlenecks and build highly efficient networks.
Hierarchical Network Design: Core, Distribution, and Access
The three-tier model ensures redundancy and efficient traffic flow:
Core Layer: The high-speed backbone connecting locations and data centers. Redundancy and fast switching prevent bottlenecks.
Distribution Layer: Connects core and access layers while managing routing, VLAN segmentation, and security filtering.
Access Layer: Where end-user devices connect. Secure switches and access points enforce policies and provide reliable connectivity.
This layered design reduces congestion, simplifies troubleshooting, and scales predictably as the business grows.
Smart Segmentation for Security & Performance
Separating traffic keeps networks secure and efficient:
VLANs isolate traffic (e.g., IoT vs. corporate) to limit risk.
Multiple SSIDs & Role-Based Access give employees, contractors, and guests the right level of access.
Dynamic VLANs automatically place users in the right segment based on login credentials.
The result: stronger security, optimized bandwidth, and controlled access to sensitive resources.
Best Practices to Reduce Bottlenecks
Smooth traffic flow requires proactive strategies:
Link Aggregation (LACP) increases bandwidth and provides redundancy.
QoS Policies prioritize voice, video, and critical applications.
Traffic Shaping ensures essential apps always get bandwidth.
AI Optimization detects and resolves bottlenecks automatically.
SD-WAN & Redundant WAN Links reroute traffic dynamically and ensure continuity during outages.
2. Proper Placement of Access Points (APs)
Proper AP placement is critical for strong, consistent Wi-Fi. Done right, it eliminates dead zones, minimizes interference, and supports high-performance connectivity. Done poorly, it leads to weak signals, congestion, and frustrated users.
RF Planning and Spectrum Analysis
Before deployment, conduct a wireless site survey to understand signal behavior in your environment. Tools like Ekahau, AirMagnet, or Cisco Meraki’s RF analysis help visualize coverage with heatmaps and adjust settings automatically.
Best practices include:
Signal Strength: Maintain -67 dBm to -55 dBm for optimal performance.
Channel Optimization: Avoid co-channel interference with intelligent channel selection.
Band Steering & Load Balancing: Direct devices to 5 GHz for faster speeds and balance clients across APs.
This proactive planning ensures seamless roaming and consistent coverage across offices, campuses, or warehouses.
Minimizing Interference
Wi-Fi signals are easily disrupted by walls, metal, industrial equipment, and even nearby networks. To reduce interference:
Use dual-band APs for more capacity.
Enable auto channel selection to adapt in real time.
Avoid excessive signal overlap to reduce congestion.
Deploy directional antennas in large or open spaces to focus coverage.
These steps help maintain reliable, high-quality wireless performance.
Planning AP Density
AP density should match user demand and application requirements.
General Offices: 1 AP per 2,000–2,500 sq. ft.
High-Density Areas: 1 AP per 500–800 sq. ft. (e.g., conference rooms, auditoriums).
Application Use: Video conferencing, VoIP, and cloud apps require more capacity.
Load Balancing: Spread users across APs to prevent overload.
The right density ensures stable, high-speed connections even in busy environments. With cloud-managed, AI-driven tools, enterprises can automate optimization and scale wireless networks without constant manual adjustments.
3. Cabling & Infrastructure Considerations
Even in a wireless-first world, Ethernet cabling is the backbone of reliable, high-performance networking. The right infrastructure ensures speed, stability, and scalability, while poor design creates bottlenecks. Smart choices in cabling, power delivery, and structured design are what keep enterprise networks running smoothly today and ready for tomorrow.
Choosing Between Cat6, Cat6a, or Fiber
Cabling type directly impacts bandwidth, distance, and resistance to interference.
Cat6 (10 Gbps up to 55m, 1 Gbps up to 100m)
Affordable and widely supported; ideal for general offices and SMBs. Best for gigabit speeds, though limited for high-bandwidth use beyond 55m.
Cat6a (10 Gbps up to 100m, better shielding)
A step up in performance and durability. Designed for high-density Wi-Fi, VoIP, and IoT-heavy environments. Slightly bulkier and pricier, but future-proof.
Fiber Optics (Up to 100 Gbps, long distance)
The gold standard for data centers, network backbones, and campuses. Immune to EMI, supports long-haul connections, but requires specialized installation and higher upfront investment.
Best practice: Use Cat6/Cat6a at the access layer (APs, VoIP, workstations) and fiber for core and distribution layers. Consider fiber-to-the-desk for extreme performance needs like trading floors or labs.
Powering Access Points and Devices: PoE vs. Traditional Power
Power over Ethernet (PoE) delivers both power and data through one cable, simplifying deployment and lowering costs. Modern switches support PoE, PoE+, and UPoE, making it easy to run APs, VoIP phones, IP cameras, and IoT devices without extra wiring.
Benefits of PoE:
Simplifies deployment by eliminating local power outlets.
Improves reliability with centralized backup power.
Cuts costs on electrical infrastructure.
Scales easily with new devices.
Traditional power is still needed in some cases, legacy switches, high-power equipment, or where local power is more stable.
Best practice: Deploy PoE+ (802.3at) for Wi-Fi 6 APs and IoT devices; UPoE (802.3bt) for high-power cameras, multi-radio APs, and advanced IoT. Always confirm PoE budgets match device requirements.
Structured Cabling Best Practices
A structured design keeps networks scalable, efficient, and easy to troubleshoot.
Hierarchical Design: Fiber at the core, Cat6a/fiber at distribution, PoE-enabled switches at access.
Cable Management: Color-coding, trays, and labeling reduce downtime and speed up maintenance.
Future-Readiness: Allow space and redundancy for Wi-Fi 6E, 400G Ethernet, AI-driven networking, and IoT expansion.
Environmental Planning: Control heat, reduce EMI exposure, and use shielded/outdoor-rated cables where needed.
4. Performance Optimization Strategies
Enterprise networks are under constant pressure, from cloud apps and IoT to remote users and real-time services. To keep performance consistent, IT teams need strategies that reduce latency, ensure availability, and allocate resources where they matter most. Advanced network gear now comes with AI-driven tools and traffic optimization features, but success ultimately depends on how these capabilities are applied.
Here are three proven strategies:
Implementing QoS (Quality of Service) Policies
QoS ensures mission-critical apps, like VoIP, video conferencing, and cloud platforms, always take priority over less urgent traffic. Without it, essential services risk latency, jitter, or dropped calls during congestion.
How it works: QoS classifies traffic, assigns priority levels, and reserves bandwidth for high-value applications. On Cisco Meraki, this includes:
Layer 7 Traffic Shaping for app-specific rules.
DSCP Marking to tag and prioritize packets.
Voice & Video Optimization for smoother calls and conferencing.
Best practices: Prioritize core apps, deprioritize non-essential traffic, and adjust settings based on real-time analytics.
Using Bandwidth Management & Traffic Shaping
Bandwidth management prevents a few devices or apps from hogging capacity. Traffic shaping smooths usage, while throttling limits low-priority apps when necessary.
Meraki features include per-device bandwidth limits, app-based shaping (e.g., throttling YouTube, prioritizing Office 365), and per-SSID controls to separate guest vs. employee traffic.Best practices: Apply shaping to non-essential traffic, enforce fairness across devices, and revisit policies regularly as usage patterns evolve.
Leveraging AI-Powered Analytics
AI takes network optimization a step further with predictive insights and automated fixes. Instead of reacting to issues, IT can let the network adjust itself.
Key benefits:
Detects anomalies before they impact users.
Balances load dynamically across APs and switches.
Offers device-level insights to pinpoint bottlenecks.
Enables “self-healing” by resolving minor issues automatically.
Best practices: Enable AI-driven alerts, use real-time health dashboards, and allow smart QoS adjustments based on live traffic data.
5. Security & Compliance for Enterprise Networks
Cyber threats evolve just as quickly as business itself. To protect sensitive data, maintain uptime, and meet compliance standards, enterprises need a multi-layered security approach built on Zero Trust principles, advanced threat protection, identity-based access, and regulatory compliance.
Cloud-managed security platforms make this possible, offering automation, AI-driven insights, and built-in compliance tools. Here are the key strategies every enterprise should adopt:
Deploying Zero Trust Security (ZTNA)
Traditional perimeter defenses are no longer enough in a world of cloud apps, remote work, and IoT. Zero Trust follows the principle: “Never trust, always verify.”
How to implement Zero Trust:
Micro-segmentation: Limit lateral movement of threats.
Least-privilege access: Grant only what each user needs.
Continuous authentication: Require re-verification for sensitive apps.
Device posture checks: Ensure devices meet security standards before access.
ZTNA tools: Replace legacy VPNs with adaptive, identity-aware access.
Firewalls for Advanced Threat Protection
Firewalls remain the first line of defense. Cloud-managed appliances like Cisco Meraki MX go beyond basic filtering with:
Intrusion prevention (IPS) using real-time threat intelligence.
Advanced malware protection (AMP) for ransomware and zero-day threats.
Geo-IP filtering to block risky regions.
Application-aware firewalling for shadow IT control.
Secure SD-WAN & Auto VPN for encrypted branch connectivity.
Best practices: Use Layer 7 firewall rules, enable threat feeds, monitor logs, and apply traffic analytics to spot anomalies.
Enforcing MFA & Identity-Based Access
Passwords alone are a liability. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds a second layer of security, like a push notification, biometric scan, or OTP, making stolen credentials far less dangerous.
Benefits:
Prevents unauthorized access.
Secures cloud apps, VPNs, and SaaS platforms.
Meets compliance requirements (SOC 2, HIPAA, PCI-DSS).
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Industries from healthcare to finance demand strict controls and audit readiness. Non-compliance risks fines and reputational damage. Cisco Meraki’s tools simplify compliance with features like:
End-to-end encryption.
Automated compliance reporting.
Centralized logging and monitoring.
Regular policy audits to align with HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and SOC 2 standards.
Future Trends in Enterprise Networking & Cisco Meraki
Enterprise networks are rapidly evolving to support more digitally mature, distributed, and dynamic environments. From AI-driven automation to edge computing, the next wave of innovation is reshaping how businesses build secure, scalable networks.
AI-Driven Automation for Predictive Network Maintenance
AI and machine learning are shifting network management from reactive to proactive. Instead of waiting for outages or slowdowns, AI-powered platforms can predict failures, spot misconfigurations, and auto-correct performance issues before users notice. For growing enterprises, this means less downtime, reduced manual effort, and IT teams freed to focus on strategic priorities.
IoT and Edge Computing in Enterprise Networking
From smart sensors to connected machinery, IoT devices are multiplying, and they demand secure, low-latency networks. Edge computing processes data closer to where it’s generated, cutting delays and reducing cloud dependency. This is especially valuable in healthcare, logistics, and retail, where real-time insights and automation can improve safety, efficiency, and customer experience.
Growth Next-Gen Wireless Networking
Advances in wireless standards are enabling faster speeds, higher capacity, and lower latency, critical for high-density environments like campuses, hospitals, and smart offices. Emerging wireless networks will better support:
Bandwidth-heavy applications like AR/VR and AI workloads.
Low-latency collaboration tools such as real-time video and virtual whiteboarding.
Smarter spectrum use, reducing congestion and improving reliability.
SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) Integration
With hybrid work and cloud-first strategies, security can no longer depend on a physical perimeter. SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) unifies networking and security into a cloud-native model that includes SD-WAN, secure web gateways, CASB, and ZTNA. The result:
Identity-based, secure access for any user, on any device, from anywhere.
Simplified management, combining networking and security under one framework.
Stronger protection against evolving cloud and edge threats.
Conclusion
As enterprise IT environments grow in complexity and scale, ensuring a network infrastructure that is secure, optimized, and future-ready is critical to long-term success. This blog post highlights how cloud-managed solutions like Cisco Meraki can serve as a strategic foundation for enterprises seeking to enhance operational efficiency, improve security posture, and scale intelligently.
By adopting best practices in network design, device placement, security implementation, and cloud management, organizations can unlock measurable benefits, from improved application performance and reduced downtime to streamlined administration and faster incident response.
Would you like to turn your network into a strategic advantage? Contact Jones IT today to schedule a free network consultation or Cisco Meraki deployment readiness review.