How SMEs Can Leverage AI Without Losing Focus On Core Business Needs
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has truly made a meteoric rise, going from Sci-Fi fancy to becoming a legitimate business mainstay. While most of the hype has been focused on generative AI applications such as chatbots and image creation, AI's real potential to transform business undoubtedly is far greater. However, the allure of easy success using AI needs to be tempered by the realities of business needs, resource constraints, and the fluidity of the technological landscape. This is especially true for small and medium enterprises (SMEs), as strategy-less AI adoption can easily overstretch their operations, diverting focus from core business fundamentals.
In this blog post, we cover the essential aspects of AI adoption to help SMEs effectively adopt and leverage AI while mitigating the risks.
Growing Role Of AI For SMEs
AI has commoditized the ability to effectively address business challenges, save costs, and boost revenue. Tools like generative AI, automated analytics, AI agents, and AI-driven platforms are transforming how businesses operate, grow, and mature. Therefore, it is not surprising that as of 2025, 78 percent of organizations use AI in at least one business function, up from 55% in 2024.
Most common applications of AI among SMEs include:
Chatbots and Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots are streamlining customer service by managing common inquiries, freeing up human agents for more complex issues.
Content Creation and Design: Generative AI tools are being used to significantly cut down the time needed to develop new marketing campaigns. These tools enable marketers to create marketing materials, graphics, blog posts, and other content quickly and efficiently.
Recruitment and HR: AI is also being used to automate tasks like screening resumes and scheduling interviews, streamlining the hiring process.
Personalized Recommendations: Thanks to AI, personalized recommendations, once a distinguishing feature of large players like Amazon and Netflix, are now available to everyone. Even small e-commerce businesses can now use AI to analyze customer behavior and recommend personalized products, increasing sales and customer engagement.
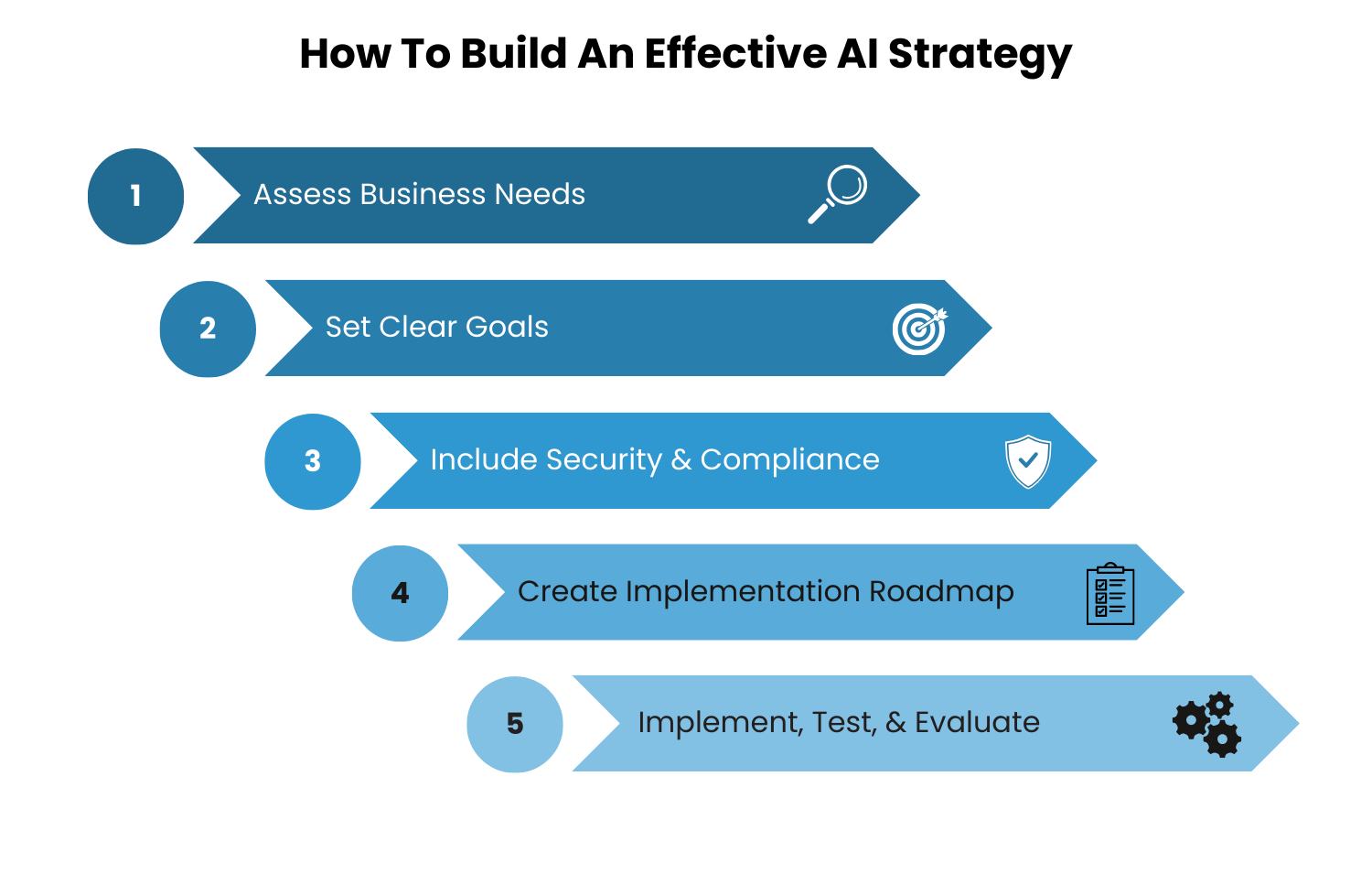
How To Build An Effective AI Strategy
Before adopting AI, SMEs should build a strategic approach taking into consideration their business needs and foundational practices. Here’s a simple 5-step roadmap for successful AI adoption.
Assess Business Needs
Before diving into AI adoption, it’s essential to start with a clear, honest look at your business needs. This step isn’t just a formality. It’s the foundation that ensures AI becomes a strategic asset rather than just the latest shiny tech. The goal is to use AI where it can solve real problems, unlock efficiencies, and create measurable business impact.
Pinpoint the Pain Points
Begin by identifying the biggest bottlenecks and inefficiencies in your operations. Which processes drain the most time and resources? Where do errors or delays happen most often? This could be anything from slow manual data entry and customer service backlogs to complex supply chain challenges or underperforming marketing campaigns. The clearer your picture of these pain points, the easier it is to see where AI can step in with high-impact solutions.
Target High-Impact AI Opportunities
Once you know the challenges, evaluate which ones can be most effectively addressed by AI. For instance, if data entry eats up hours, automation tools can drastically cut both time and errors. If customers face long wait times for support, AI-powered chatbots or virtual assistants can help resolve common issues instantly. AI shines in areas with large amounts of untapped data, where its ability to spot patterns, forecast outcomes, and automate processes can directly improve performance and reduce costs.
Keep AI Aligned with Your Strategy
This assessment must be underpinned by your business goals. AI should never be a stand-alone experiment. It must tie directly to your business objectives. Whether your aim is to grow revenue, improve customer satisfaction, reduce costs, or expand into new markets, AI should be an enabler.
For example, if your goal is market expansion, AI can accelerate research and identify high-potential prospects. If improving product quality is the priority, predictive maintenance or anomaly detection could be instrumental. By keeping AI initiatives aligned with your larger goals, you ensure that each investment supports your business goals and delivers lasting value.
2. Set Clear Goals
The next step is to define exactly what success looks like. A vague goal like “improve efficiency” won’t cut it. You need specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives that tie directly to your core business priorities.
Set Clear, Measurable Outcomes
Decide upfront how you’ll measure success. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) before implementation so you can track progress with precision. For example, a customer service AI project might aim to reduce average wait times by 20% within six months or increase first-contact resolution rates by 15%. For sales, a goal might be to boost lead conversion rates by 10% using AI-driven lead scoring.
Know Your Starting Point
Identify your current performance metrics to create a baseline. This is an important step because it not only helps you measure progress but also makes it clear whether AI is truly delivering value. Without this starting point, you risk chasing phantom improvements that don’t translate into real results.
Focus on Tangible Business Value
Every measurable outcome should directly support your broader business strategy. Whether it’s reducing operational costs, increasing revenue, improving customer satisfaction, or strengthening market position, AI should always serve a clear purpose.
3. Include Security and Compliance From the Very Beginning
When integrating AI into business operations, security and compliance shouldn’t be afterthoughts. Trying to “bolt on” these safeguards later is far more complex, costly, and less effective. By prioritizing them early, you create a resilient AI infrastructure that protects sensitive data, upholds customer trust, and meets both legal and ethical standards.
Build Security from the Ground Up
Start with clear, comprehensive security policies that govern every stage of AI operations, such as data handling, access control, system design, and incident response. This means defining protocols for encryption, secure API connections, network segmentation, and regular audits. Pay special attention to safeguarding customer information, proprietary data, and intellectual property. Security is not just about technology, it’s also about people. Ensure staff receive training on best practices, use strong authentication methods, and know how to report and address vulnerabilities.
Understand and Meet Compliance Obligations
AI systems often process sensitive and regulated data, making compliance a non-negotiable necessity. So, you will need to identify all relevant requirements based on your industry, location, and the type of data you handle. Here’s what you need to consider:
Data Protection Laws: GDPR for the EU, CCPA in California, and other regional privacy laws that dictate how personal data must be collected, stored, and processed.
Industry-Specific Standards: Healthcare must comply with HIPAA, while financial services face frameworks like SOX or PCI DSS.
Ethical AI Guidelines: Even when not legally binding, follow principles of fairness, transparency, and bias prevention to help strengthen stakeholder trust and brand reputation.
Data Governance Frameworks: Maintain high data quality, document data lineage, and set retention policies to ensure AI systems operate on reliable, compliant information.
By embedding security and compliance into your AI strategy from the start, you minimize risks such as data breaches, legal penalties, and reputational damage, while creating a strong foundation for responsible innovation. This proactive approach enables AI to deliver value without compromise, supporting both business growth and long-term trust.
4. Create An Implementation Roadmap
A well-defined, strategic implementation roadmap is arguably the most critical element of an effective AI strategy. A phased approach here will help keep AI adoption structured, manageable, and aligned with long-term objectives, ensuring that AI becomes an enabler, not a distraction.
Start with the Low-Hanging Fruit
Begin by targeting areas where AI can deliver quick, visible results with minimal disruption. These are typically repetitive, time-consuming tasks or processes that can be automated for instant efficiency gains, such as email categorization, routine report generation, or customer service chatbots for common inquiries. Tackling these early wins builds confidence, proves the value of AI, and creates valuable learning experiences before moving into more complex applications.
Select the Right Tools for the Job
With countless AI tools on the market, ranging from plug-and-play software to advanced custom platforms, choosing the right fit is critical. Assess solutions based on your specific needs, budget, technical capacity, and future scalability. Look for tools that integrate seamlessly with existing systems, provide strong vendor support, and prioritize data security. Start with simple, user-friendly tools that match your initial “quick win” projects, then scale up as your AI maturity grows.
Secure the Expertise You Need
AI success overwhelmingly depends on having the right skills. SMEs have two main options:
Build In-House Expertise: Invest in training current employees, hiring AI-skilled talent, or creating mentorship programs. This approach builds long-term capability, deepens AI understanding within your business context, and ensures alignment with company culture.
Outsource Strategically: For immediate needs or specialized projects, AI consultants and experienced MSPs, like Jones IT, can deliver high-quality solutions without the overhead of permanent hires. This is particularly effective for pilot projects or niche AI applications. Just ensure project scopes, deliverables, and security protocols are clearly defined from the start.
By combining quick wins, well-chosen tools, and the right expertise, SMEs can adopt AI at a sustainable pace, maximizing value, minimizing risk, and setting the stage for more ambitious initiatives in the future.
5. Implement, Test, And Evaluate
Implementing AI isn’t a one-time event. It’s an ongoing process of deployment, testing, and refinement. To ensure AI continues to deliver value and stays aligned with your business objectives, you need a structured framework that supports smooth adoption, reliable performance, and continuous improvement.
Implementation: Laying the Groundwork for Success
Phased Rollout: Avoid the risks of an all-at-once launch. Start with a pilot in one department or a specific use case to test performance and iron out issues before scaling up.
Seamless Integration: Ensure the AI solution fits smoothly into your existing systems and workflows, smoothing employee learning curves and preventing data silos.
Employee Training & Adoption: Equip staff with the skills and confidence to use AI effectively. Show how AI enhances their capabilities rather than replacing them, building trust and enthusiasm.
Data Quality First: AI is only as strong as its data. Invest in clean, accurate, and relevant datasets, and establish processes to maintain data quality over time.
Testing: Ensuring Reliability and Fairness
Pre-Deployment Testing: Validate AI performance in a controlled environment before going live, checking for accuracy, scalability, and security.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Involve real end-users to test usability and functionality, ensuring the solution meets practical needs.
Edge Case & Bias Testing: Go beyond standard scenarios, testing how the AI handles rare situations and actively checking for algorithmic biases to prevent unfair outcomes.
Evaluation: Measuring Impact and Staying Agile
Ongoing Performance Monitoring: Regularly assess AI’s effect on productivity, costs, customer satisfaction, and employee morale, not just its initial performance metrics.
Track KPIs: Measure outcomes directly tied to business goals, such as customer resolution time, lead conversion rates, or marketing ROI.
Refine and Adapt: Use evaluation insights to fine-tune algorithms, explore new use cases, or pivot to different solutions when needed.
Feedback Loops: Keep communication open between users, developers, and business leaders so real-world insights feed continuous improvement.
Measure ROI: Weigh the benefits, revenue growth, cost savings, efficiency gains, against implementation and maintenance costs to ensure value creation.
Ethical Oversight: Maintain transparency, accountability, and fairness in AI operations to safeguard trust and compliance.
By approaching AI implementation as an evolving process, anchored in strong planning, rigorous testing, and regular evaluation, you can maximize returns, mitigate risks, and ensure AI remains a strategic asset that strengthens your competitive edge.
Examples of AI Use Among SMEs
Here are some of the most common AI applications:
AI Chatbots for Customer Support
AI-powered chatbots are transforming customer service by providing instant, 24/7 assistance. They can handle frequently asked questions, guide customers through processes, and perform basic troubleshooting, freeing human agents to focus on more complex issues. As the AI learns from each interaction, chatbots become more accurate and helpful, improving customer satisfaction while reducing operational costs.
Content Creation with Generative AI
Generative AI tools help businesses scale content marketing efforts without expanding their teams. By supplying an outline or a few keywords, businesses can quickly produce blog posts, social media updates, product descriptions, and email campaigns. This speeds up content production, maintains brand consistency, and ensures a strong online presence, while saving time and resources.
Task Scheduling and Optimization
AI-driven scheduling tools can analyze calendars, deadlines, and resource availability to recommend optimal meeting times, project timelines, and task assignments. They can spot bottlenecks in advance and suggest reallocations to keep projects on track. For service-based businesses, this can also mean optimizing delivery routes, appointment bookings, or technician schedules, resulting in faster service and better use of resources.
Note-Taking and Meeting Transcripts
AI transcription and smart note-taking tools capture conversations in real time, identify speakers, and generate accurate, searchable transcripts. Many AI tools can also summarize key points and action items, ensuring that decisions and insights are never lost. This reduces the need for manual note-taking and allows participants to stay fully engaged in discussions.
AI-Assisted Coding
For SMEs with software development needs, AI-assisted coding tools can speed up production and improve quality. They offer real-time code suggestions, detect errors, automate repetitive tasks, and even generate functional code from plain language prompts. This accelerates development cycles, reduces bugs, and allows developers to focus on strategic, high-value projects, while lowering the barrier for non-developers to contribute to technical initiatives.
Common AI Adoption Challenges For SMEs
While AI adoption can be transformative, it’s not without its hurdles. Understanding these challenges upfront can help businesses plan effectively and avoid costly missteps.
Complexity
Without well-defined objectives, AI can create more problems than it solves. This is especially problematic for businesses that lack the in-house expertise to navigate AI’s technical demands like selecting the right models, integrating them with existing systems, and understanding the associated risks. This complexity can extend timelines, increase costs, and dilute the expected benefits. The initial excitement over AI’s potential can quickly give way to frustration if the technology isn’t aligned with clear, measurable business goals.
2. Cost
AI adoption often requires a significant financial commitment. Beyond the technology itself, there are expenses related to data collection and processing, infrastructure, and specialized talent. For SMEs with limited budgets, these costs can be a barrier to entry as ROI may be difficult to demonstrate in the short term, which makes it harder to justify the investment. Hidden costs like ongoing maintenance, training, or the fallout from a potential data breach, can further strain resources.
3. Security And Compliance
AI systems rely on large datasets, often containing sensitive or proprietary information. This raises critical concerns about data security, privacy, and compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Recent events, such as Google inadvertently indexing publicly shared AI chats, underscore the potential for unintended consequences when data handling is left unchecked.
Given the fluidity of the AI landscape, SMEs may find it challenging to implement strong protections against cyber threats or to navigate complex regulatory requirements. Non-compliance risks steep penalties and reputational damage. Moreover, ethical considerations such as mitigating bias, ensuring transparency, and safeguarding user trust add yet another layer of responsibility.
4. Over-Reliance
While AI can greatly enhance efficiency, leaning too heavily on automated decision-making without human oversight can be risky. Over-dependence may erode critical thinking, creativity, and adaptability, qualities that are essential for responding to unexpected situations. Striking the right balance between AI automation and human judgment is key to ensuring that AI augments rather than hinders human capabilities.
Conclusion: Balancing Innovation With Practicality
AI offers SMEs immense potential, but success depends on using it strategically, not chasing every new tool. The goal is to enhance core business functions, solve real problems, and deliver measurable results.
Key Principles for Sustainable AI Adoption:
Keep Human Ingenuity Central – AI should enhance human creativity, intuition, and problem-solving. Use it to free people for higher-value, strategic work.
Align with Existing Goals – Adopt AI that integrates seamlessly into current processes and supports business objectives, avoiding unnecessary disruption.
Focus on Real Problems – Implement AI where it addresses clear pain points rather than using it for its own sake.
Plan for Longevity – Ensure you have the resources, skills, and infrastructure to maintain, update, and scale AI systems over time. Without this, even promising tools can become burdens.
A measured, problem-first approach ensures AI strengthens the business, sustains innovation, and delivers lasting value.
AI should work for you, not the other way around. Discover how to implement solutions that integrate seamlessly, scale sustainably, and deliver real value. Schedule a call today.